Direct Satellite-to-Smartphone Connectivity on the Horizon
Mar 21, 2025
AST SpaceMobile’s satellite-based cellular broadband technology fundamentally alters the way our world is connected, without the reliance on traditional infrastructure types to provide mobile connectivity. It’s designed to connect billions of users in the most remote and underserved parts of the world directly through their existing smartphones without additional equipment. This direct-to-smartphone capability resolves a longstanding connectivity problem that satellite and terrestrial solutions for such have not done well in addressing effectively, through seamless integration with existing mobile devices and networks. A key piece of the technology’s value lies in its ability to maintain connection during disasters or in those places where terrestrial infrastructure is destroyed, where such resilience allows for emergency communications that can save lives during catastrophic events when conventional networks crumble.
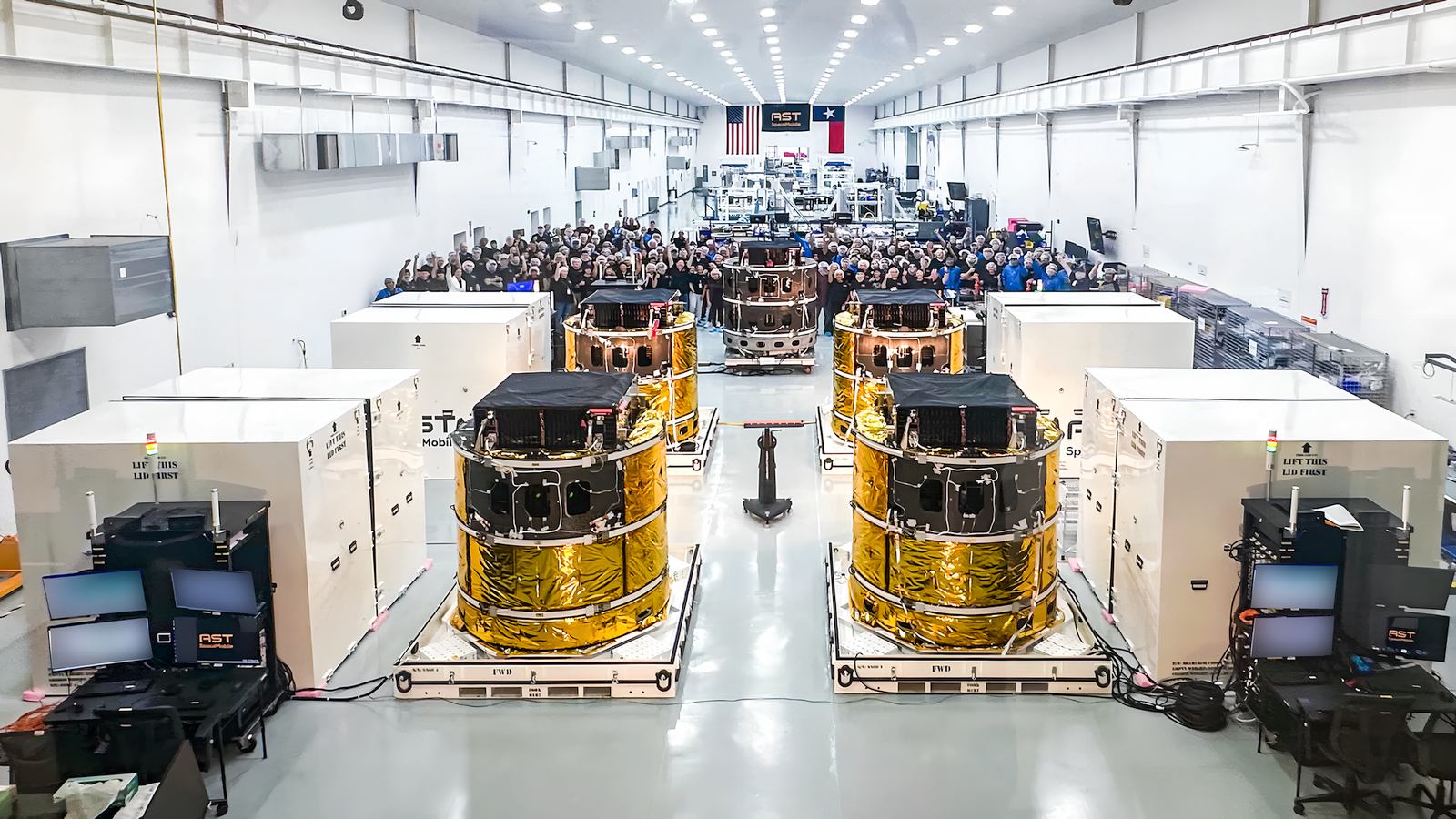 August 5, 2024: Final stage of construction for five BlueBird satellites. Credit: AST SpaceMobile
August 5, 2024: Final stage of construction for five BlueBird satellites. Credit: AST SpaceMobile
Strategically, the European joint venture with Vodafone positions AST SpaceMobile to become a sovereign European space asset by using existing cellular spectrum agreements in multiple countries. The technology offers great improvements in regional connectivity resilience by constructing a dedicated European gateway infrastructure, which could reduce the digital divide between urban centers and rural communities across the continent. In addition to production capacity, this 5,600-square-meter space at which the company manufactures its space communications systems in Barcelona is a real demonstration of commitment to European technological sovereignty that generates high-skilled jobs and potentially creates local expertize in advanced space communications technology.
Strategic Value in European Space Independence
Direct-to-smartphone satellite technology offers unique strategic value in times of heightened geopolitical tensions by addressing critical infrastructure vulnerabilities. European nations can reduce dependence on foreign satellite networks while maintaining essential communications during international disputes or sanctions. This approach aligns with the EU’s IRIS² constellation initiative, enhancing space-based digital infrastructure resilience against both technical failures and security threats. Recent events demonstrate the importance of communication sovereignty, as seen with concerns about U.S.-based Starlink services in Ukraine, where Eutelsat’s stock tripled based on expectations that its OneWeb constellation would provide more reliable broadband. Similarly, Ontario’s termination of a $68 million Starlink contract following U.S. tariffs further illustrates how geopolitical tensions can significantly impact satellite connectivity access and reliability.
Given the traditional infrastructure expansion costs that are prohibitively expensive in mountainous, remote, or sparsely populated areas, satellite-based approach is cost advantageous approach. Integrating with AST SpaceMobile’s network provides European telecom operators with expansion opportunities without the need for massive capital expenditures on tower infrastructure and potentially a change in business model and ability to offer new service improvements in markets that are currently unprofitable. This kind of commercial partnership adds undeniable weight to the European space sovereignty movement because it shows that independence from foreign technologies is possible through strategic industrial collaboration rather than simply government-funded initiatives.
Technical Capabilities and Practical Applications
Today’s massive 64-square-meter Block 1 BlueBird satellites in orbit demonstrate unprecedented antenna technology that enables direct smartphone connectivity without the use of specialized user equipment to solve one of the most challenging problems in satellite communications. True 5G connectivity from space at speeds of up to 120 Mbps, sufficient for video streaming and such bandwidth-hungry applications as previously were not possible with the satellite connection to a phone, will be possible with the planned Block 2 satellites, which have three times the surface area and ten times the capacity increase. A comprehensive solution, as compared to competing satellite-to-phone services, the continuous global coverage model requires 45 to 60 satellites for the US market alone.
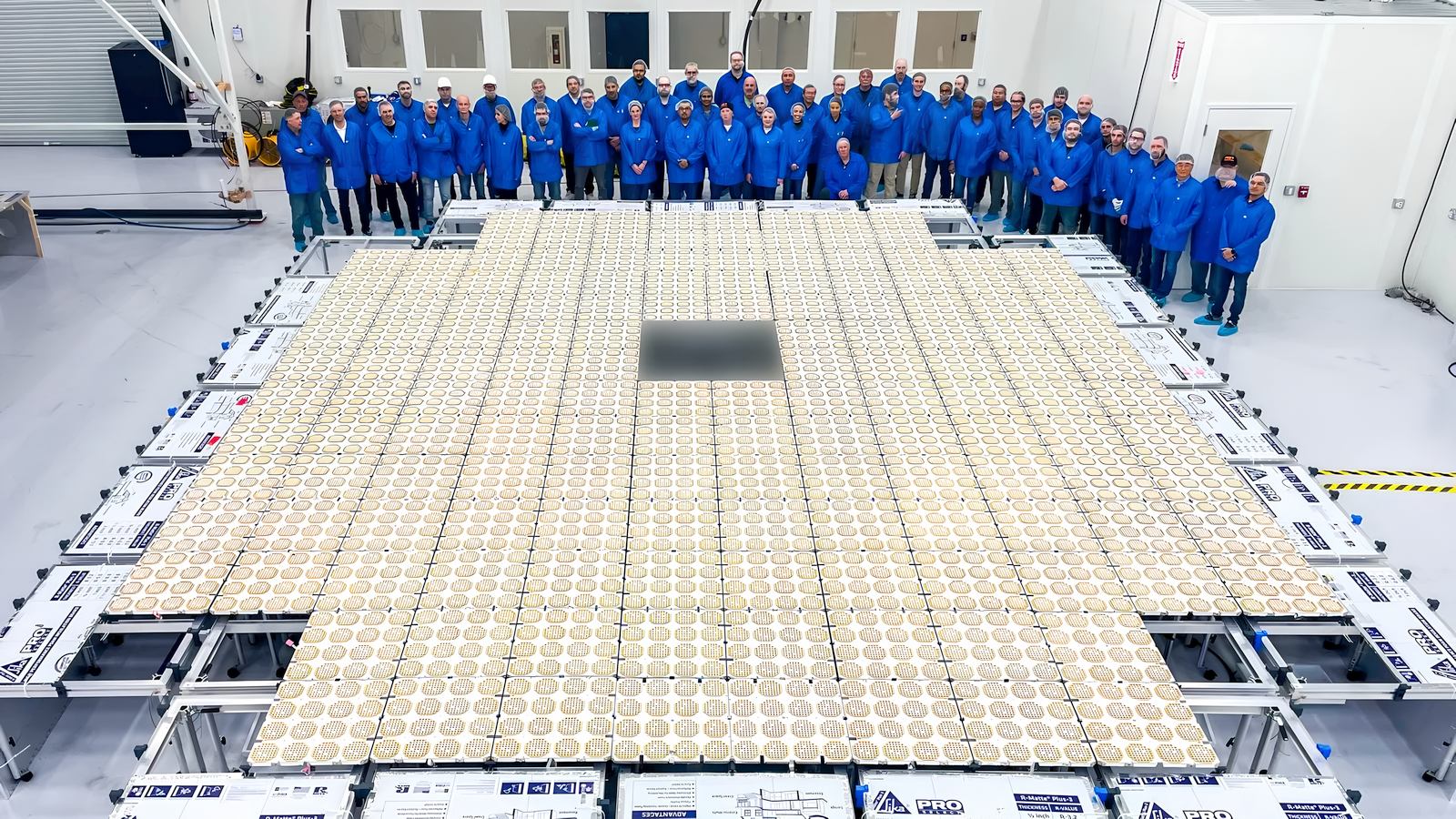 BlueWalker 3 features a 64-square-meter phased array antenna for direct mobile phone connectivity. Credit: AST SpaceMobile
BlueWalker 3 features a 64-square-meter phased array antenna for direct mobile phone connectivity. Credit: AST SpaceMobile
This opens the doors to virtually unlimited number of potential users from circulating millions into billions, and the technical capability to serve standard smartphones instead of specialized satellite phones enables emergency services, remote workers, travelers, shipping operations, and spare communities the world over. Seamless handover between terrestrial and satellite coverage integration with existing mobile networks can eliminate dead zones and thus provide continuous connectivity for users without manual network switching or their knowledge of which network provides service. By being compatible with standard cellular protocols, operators can use their existing spectrum licenses and services in new areas, and without extending into currently inaccessible areas, operators can create new revenues streams while fulfilling universal service obligations, most often mandated by regulatory authorities.
Manufacturing Innovation and Economic Implications
The company’s vertically integrated manufacturing approach, with facilities in Texas, Florida, and now Spain, represents a new model of space industry that emphasizes volume and efficiency rather than traditional bespoke satellite construction methods. By late 2025, the ambitious production scaling from two to six satellites monthly shows manufacturing innovation that is rarely seen in the space sector, and it has the potential to change how satellite constellations are deployed and how quickly time to market can be achieved for space-based services. The size of this manufacturing operation is further reflected in the substantial capital expenditure of $150-175 million quarterly, which is one of the largest commercial satellite production operations outside government programs.
 AST’s HQ and U.S. manufacturing 85,000 sq. ft. facility in Midland, TX. Credit: AST SpaceMobile
AST’s HQ and U.S. manufacturing 85,000 sq. ft. facility in Midland, TX. Credit: AST SpaceMobile
Direct economic benefits from such investment are generated through job creation but also knowledge transfer and technological capacity building, which contribute to strengthen the overall European space industry competitiveness. By manufacturing in house, there is more control over supply chains that may be able to avoid the global component shortages and manufacturing delays that have plagued other satellite constellation deployments. This $1 billion cash reserve is evidence of massive investor confidence in the technology’s commercial viability and gives it runway to continue expanding and refining the technology without an immediate revenue pressure.
Market Potential and Competitive Positioning
The direct-to-smartphone satellite connectivity market is a potentially game-changing opportunity within the broader telecommunications sector, with mobile network operators especially looking to provide coverage expansion through the use of the technology without the need for traditional infrastructure investment. AST SpaceMobile targets dual markets of the commercial and government sectors, creating multiple revenue streams to hedge against the risks of the market niche, and the recent $43 million defense contract illustrates that government is interested in the technology due to its unique capabilities. Strategically, the European focus puts the company in a good position to take advantage of EU digital infrastructure initiatives and regulatory frameworks that are increasingly focusing on technological sovereignty.
AST SpaceMobile’s direct-to-smartphone satellite technology represents a potentially revolutionary advancement in global telecommunications with European strategic value for space sovereignty. It’s the technology that is based on novel designs for satellites, vertically integrated manufacturing, and strategic relationships with established operators that may improve availability of mobile communications in regions that had previously remained underserved. Regulatory and technical hurdles remain around the company’s ambitious plans, but with its massive financial resources, manufacturing expansion, and alliances with both commercial and government customers, the company is in a unique position at the meeting place between space technology innovation and practical telecommunications application, providing a tantalizing picture of universal connectivity that could reshape the satellite and mobile communications industries in the next decade.