What Challenges Lie Ahead for Direct-to-Smartphone in EU?
Feb 22, 2025
On February 19, 2025, the Luxembourg-based satellite operator OQ Technology achieved a significant milestone as the European Union-backed accelerator announced potential funding of up to €17.5 million ($18.2 million). The funding package includes a secured €2.5 million grant from the European Innovation Council (EIC) Accelerator program and potential equity financing of up to €15 million for the company’s ongoing Series B funding round. The Series B is ambitious and aims to raise between €35 and 40 million, already backed by the Luxembourg government.
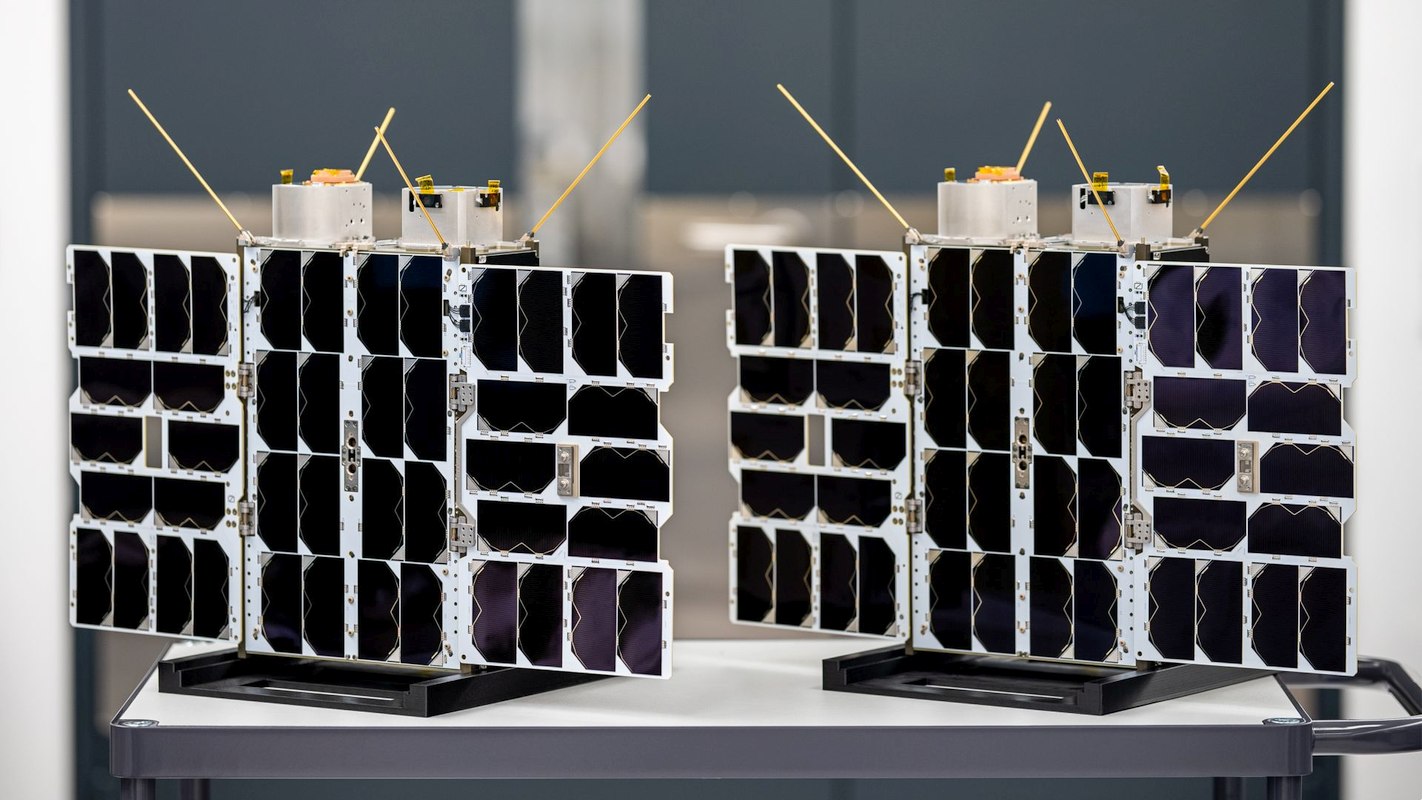 Tiger-7 & Tiger-8 LEO Satellites. Credit: OQ Technology
Tiger-7 & Tiger-8 LEO Satellites. Credit: OQ Technology
A convertible loan structure has been committed by a portion of the funding round through the Luxembourg Space Sector Development (LSSD), co-managed by the government and satellite operator SES. Under this arrangement, LSSD will convert their investment into company shares within two years of the round closing. Existing investors, including Aramco’s venture capital division, also weigh in with their participation.
Strategic Evolution and Technical Infrastructure
Since the Series A funding round in 2022, OQ Technology has shown consistent growth, raising about $13 million. The deployment of ten low Earth orbit satellites was enabled by these funds for their narrowband connectivity services for Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Particularly noteworthy is the company’s infrastructure compatibility with a multitude of off-the-shelf IoT devices running on 5G protocols. These initial deployments have proven their technical approach and that their business model is viable in the competitive satellite communications market.
In addition to the current plans, the company is planning to deploy twenty more satellites by the end of 2026 to expand the constellation coverage and performance. This expansion is crucial for sectors such as oil and gas, where off-grid device connectivity must be reliable. Besides, the company’s approach toward scaling its infrastructure is a compromise between an immediate market need and a potential technology solution for the future. Through the use of a phased deployment strategy, continuous service improvement can be made while maintaining operational efficiency and reliable coverage for existing customers in multiple industry sectors.
Technical Challenges and Innovation
OQ Technology’s efforts also include developing capabilities to connect unmodified smartphones directly with their satellite constellation. This is a challenging endeavor with respect to increased satellite power requirements and the Doppler effect. In this direction, the company has obtained a dedicated contract from the Luxembourg government to conduct feasibility studies. Their current capabilities in IoT connectivity are shown by the technical specifications of their existing eight 6U cubesats and two more scheduled for launch. However, a significant number of upgrades are needed for payload and software systems to transition to smartphone connectivity. First, the company has already successfully tested their upgraded payload in a representative environment, and the first enhanced satellite will be launched in 2026.
 TrackMe 5G IoT NTN: sleek, credit card-sized tracker for OQ satellites via SIM card. Credit: OQ Technology
TrackMe 5G IoT NTN: sleek, credit card-sized tracker for OQ satellites via SIM card. Credit: OQ Technology
Opportunities and challenges in the direct-to-smartphone market exist for OQ Technology. U.S.-based providers that are already testing beta services are now competing with the company. Nevertheless, OQ Technology’s strategic approach of starting with IoT services and moving into direct-to-mobile later on has set them apart from competitors who have already invested significantly in broadband and direct-to-mobile solutions from scratch. This sector cannot be overstated without the importance of terrestrial partnerships. As the average revenue per user (ARPU) is projected to be around $1, industry experts point out that successful partnerships with a mobile network operator can provide access to millions of potential subscribers, which is very important. But these partnerships also have technical hurdles, especially regarding interference risks when using terrestrial frequencies from orbit.
Regulatory Landscape and Market Potential
The development of direct-to-smartphone services is dependent on the regulatory environment. Regulatory frameworks await clear guidelines from bodies such as the Federal Communications Commission, which will then dictate global administrative approaches. Interference risk management and exclusion zone setting are huge regulatory challenges that could impact service availability and market attractiveness. However, the complexity of this regulatory landscape is compounded by the fact that OQ Technology needs to coordinate with numerous national telecommunications authorities, particularly in areas where it intends to widen the scope of its services. While the company has a European base, global expansion will need to be carefully managed in terms of the varying regional regulations.
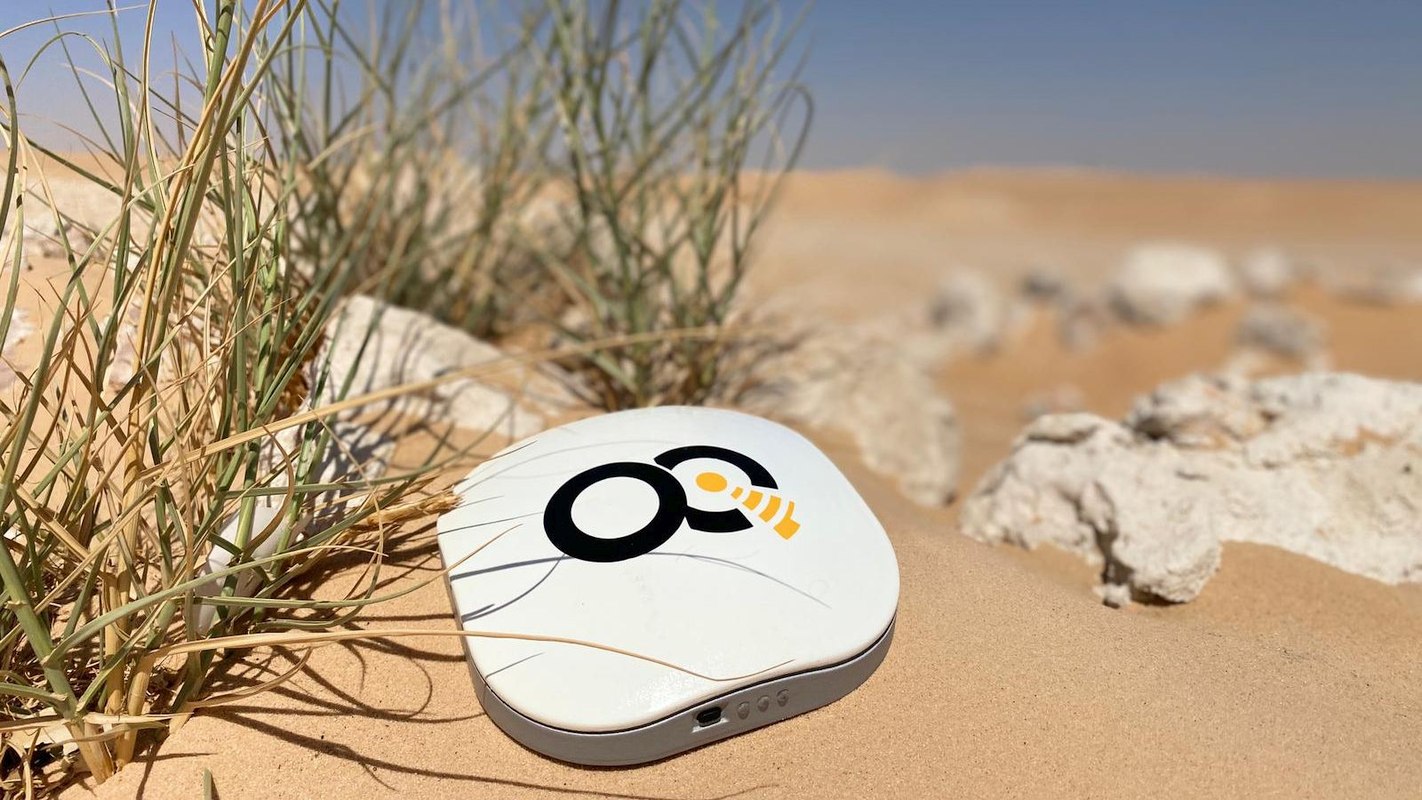 OQ terminal in the desert. Credit: OQ Technology
OQ terminal in the desert. Credit: OQ Technology
Given the successful progress to address technical, financial, and regulatory hurdles, a potential space-based connectivity market size of $100 billion could be realized. The opportunity presented by this market drives further innovation and investment in this sector, albeit in the face of significant challenges in closing connectivity gaps across areas beyond more traditional cellular coverage. Considering the growing demand, especially in underserved remote regions, this market estimate is likely to be conservative. The market is driven by the growing adoption of IoT devices in industrial applications and the demand for reliable backup communications systems, which offers multiple revenue streams to the companies that successfully navigate the regulatory landscape, say industry analysts.
Strategic Growth in a Competitive Landscape
The unique opportunities and challenges of being a European innovator in a U.S.-dominated market are created by the company’s strategic position. Strategic foresight and technical pragmatism combine to show how their methodical approach to market entry features the path of least resistance: starting with IoT services and moving on to direct-to-smartphone connectivity. With recent funding developments and government support, their plans are in good shape. In addition, the company’s location in Luxembourg, a country that has a favorable space industry ecosystem and is home to major players such as SES, offers further strategic advantages in terms of regulatory understanding and networking opportunities within the industry. The European Union institutions and national governments have been groomed into a robust support system for their technological advancement through the careful cultivation of relationships.
Their ability to overcome the complex technical, regulatory, and market challenges more effectively than their competitors will be key to the company’s success. Their presence in the IoT market is already established, alongside their innovative example in direct-to-smartphone technology, positioning them favorably for future growth. Nevertheless, for them to succeed, their agility to cope with technical challenges, forge partnerships, and stay ahead of the competition will play a significant role in unlocking their full potential.