How Will This Impact Japan's Space Capabilities?
Jan 13, 2025
Toyota made a major step in space technology when the car manufacturer declared its investment in the Japanese rocket company Interstellar Technologies. The statement disclosed that on January 7, Woven by Toyota (WbyT), the mobility subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation, had invested 7 billion yen ($44.3 million) in Interstellar. The investment proved that Toyota is set on growing its horizons beyond ground transport as the firm stated that this move aligned with their mobility strategy.
 Interstellar Technologies Promo. Credit: Interstellar Technologies Inc.
Interstellar Technologies Promo. Credit: Interstellar Technologies Inc.
It was actually started in 2020 by personnel exchanges, but this new financial investment was a step up in their cooperation. The companies pointed out that their main priority would be to bolster the supply chain in an effort to bring about mass rocket production, with WbyT (Woven by Toyota) becoming the lead investor in Interstellar’s Series F round and gaining a seat for a company director. This organisational change was particularly relevant given the growing rivalry in the global space industry and emerging demands for solutions to manufacturing challenges. It also marked a development in the space industry of Japan; both companies stated that they would work to improve Japan’s space capabilities. Experts in this industry observed that this partnership could redefine the competition within the framework of the space industry globally and especially in the Asian region where so many countries were jostling for a superior place in space technology.
Manufacturing Innovation
Interstellar’s CEO Takahiro Inagawa said that with WbyT, it was the right partner to help transform rocket production from the first unit manufacturing to a scalable production process. The collaboration was expected to bring Toyota’s vast manufacturing experience to the table to revolutionize rocket manufacturing processes and proposing that Toyota’s efficient mass production model could adapt the space technology manufacturing.
 Interstellar Technologies Promo. Credit: Interstellar Technologies Inc.
Interstellar Technologies Promo. Credit: Interstellar Technologies Inc.
The cooperation was focused on the domestic launch vehicles, and the plans were made to contribute to the Japanese government’s goal of about 30 launches per year in 2030s. This goal was quite logical taking into account the increasing interest to launch services and Japan’s desire to become more than just a player in the space business. The partnership pointed out that Toyota’s production efficiency would be vital in achieving these goals. Both the companies’ engineers were trying to incorporate Toyota’s lean manufacturing principles on the peculiarities of rocket construction, while at the same time striving to ensure the painstaking quality and reliability that is required in space work.
Technical Developments
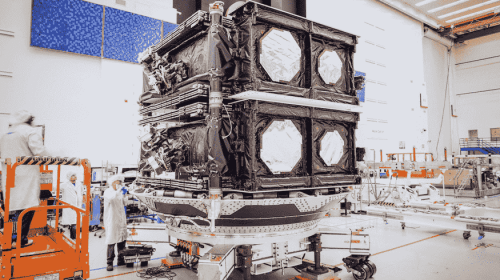
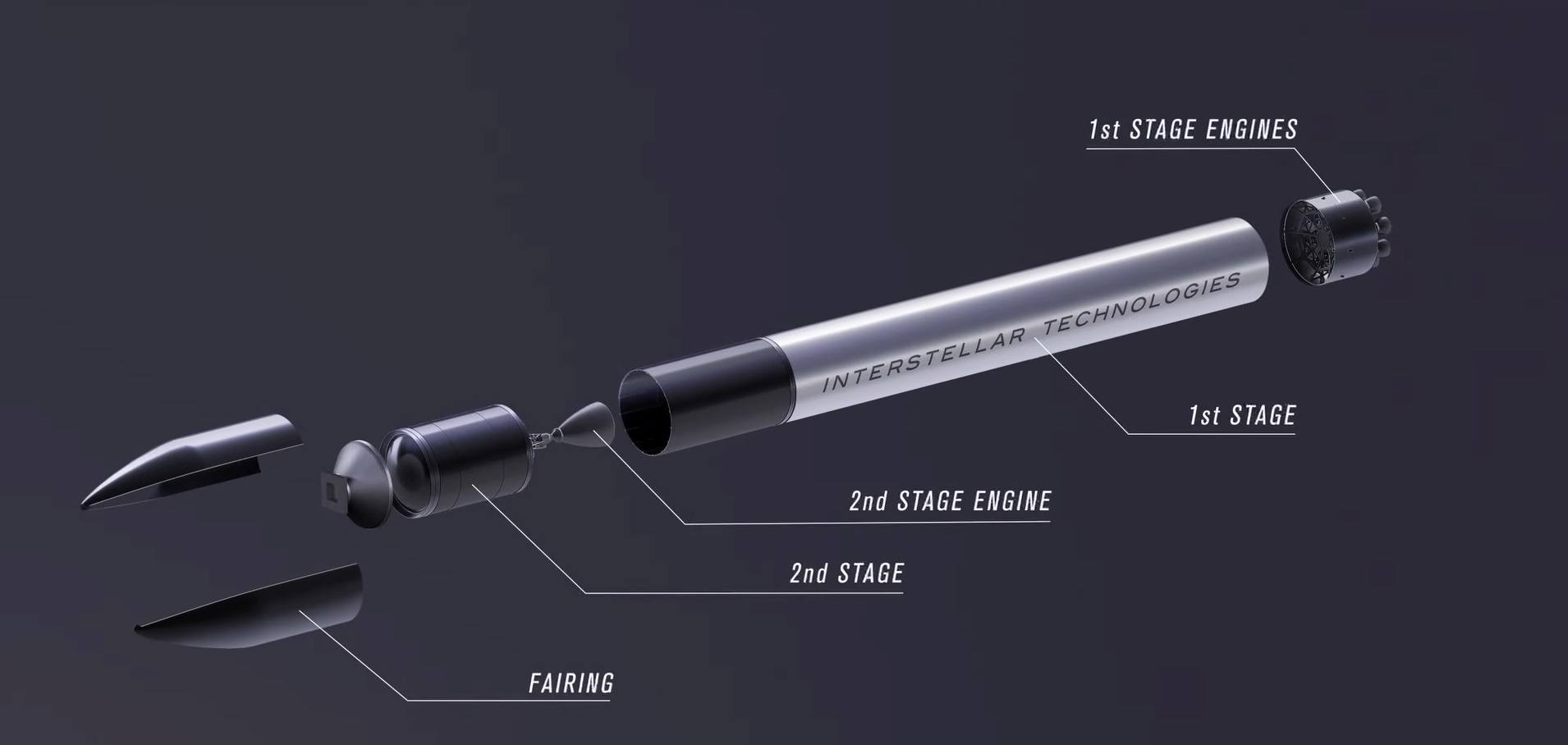
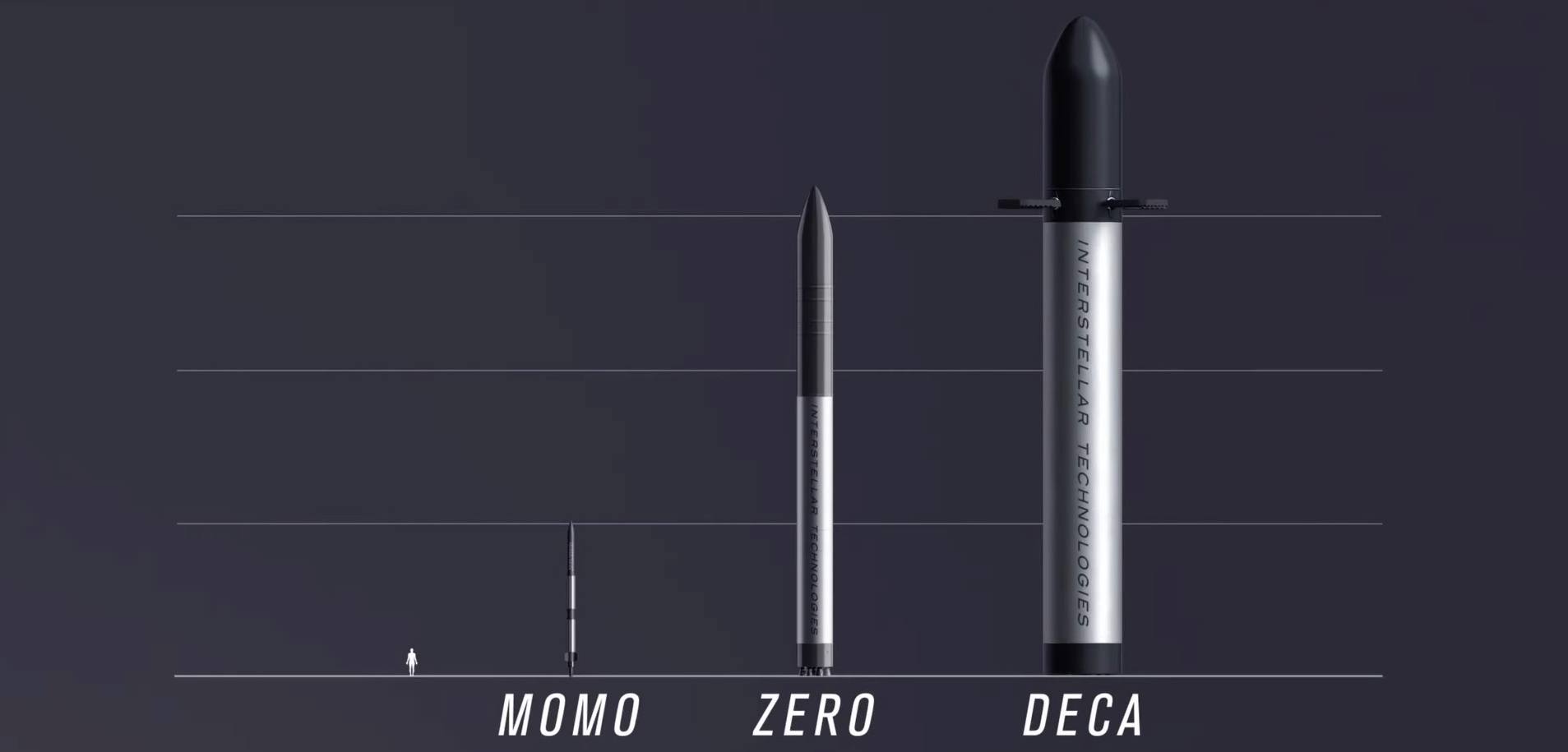
Interstellar Technologies had already demonstrated significant progress in aerospace innovation, particularly through their development of the Zero suborbital-class rocket. The technical specifications revealed that the rocket featured a 3.6-meter-high and 1.7-meter-diameter fairing made of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP). A successful fairing separation test at the Fukushima Robot Test Field in February 2023 had marked a crucial milestone in the rocket’s development.
 Interstellar Technologies Promo. Credit: Interstellar Technologies Inc.
Interstellar Technologies Promo. Credit: Interstellar Technologies Inc.
The Zero rocket’s design incorporated sophisticated engineering solutions, including a sandwich structure combining CFRP with an aluminum core material for the fuselage. The rocket’s capabilities included an impressive 800-kilogram payload capacity for low-Earth orbit missions. Furthermore, the company had begun development of an advanced reusable heavy lift rocket called Deca, planned for operations in the 2030s, which would build upon the technologies and production methods established through their earlier rockets. Recent advances in materials science and manufacturing techniques had enabled significant improvements in rocket design and construction. The partnership was exploring new applications of composite materials and advanced manufacturing processes that could potentially reduce weight while increasing structural integrity and performance. These innovations were expected to contribute to more cost-effective and efficient space launch capabilities.
Broader Industry Impact
The space launch market had shown remarkable growth, with Interstellar reporting 116 launches in the United States, 63 in China, and three in Japan during 2023. This data highlighted the competitive nature of the industry and the potential opportunity for new players with innovative approaches. The partnership between Toyota and Interstellar represented a significant step toward establishing Japan as a major contributor to the global space launch market.
The collaboration also demonstrated the increasing convergence of automotive and aerospace technologies, particularly in advanced materials and manufacturing processes. Toyota’s expertise in composite materials, evidenced by their work with Joby Aviation and various automotive applications, positioned them well to contribute to aerospace manufacturing innovation. The partnership suggested that traditional automotive manufacturing expertise could be successfully adapted for space technology production. Industry experts predicted that this convergence of automotive and aerospace technologies could lead to significant breakthroughs in manufacturing efficiency and cost reduction. The potential for cross-industry innovation was particularly promising, as solutions developed for space applications could potentially benefit terrestrial transportation and vice versa.
Future Vision
Toyota’s commitment to space technology aligned with their broader vision for future mobility, exemplified by their Woven City project at the base of Mt. Fuji. This innovative laboratory city was designed to facilitate research and development across four key areas: people, goods, information, and energy, indicating Toyota’s comprehensive approach to future transportation solutions. Woven by Toyota CEO Hajime Kumabe described the investment in Interstellar as part of the company’s evolution beyond automotive manufacturing into a comprehensive mobility company. The expanding portfolio, which included investments in various transportation technologies from land to sea to air, demonstrated their commitment to pushing the boundaries of traditional mobility concepts. The development of the Woven City project alongside space technology investments showcased Toyota’s holistic approach to future mobility solutions. The company was actively exploring how technologies developed for space applications could benefit urban development and sustainable transportation systems, creating a unique synergy between terrestrial and space-based innovation.
 Interstellar Technologies Promo. Credit: Interstellar Technologies Inc.
Interstellar Technologies Promo. Credit: Interstellar Technologies Inc.
The strategic partnership between Toyota and Interstellar Technologies represents a transformative moment in the aerospace industry, combining Toyota’s manufacturing expertise with Interstellar’s innovative rocket technology. This collaboration not only promises to advance Japan’s space launch capabilities but also demonstrates how traditional automotive manufacturing principles can be successfully adapted for aerospace applications. The partnership’s focus on mass production and supply chain optimization suggests a future where space technology becomes more accessible and commercially viable, potentially revolutionizing the global space industry while supporting Japan’s ambitious target of 30 launches annually by the early 2030s. The investment also highlights Toyota’s successful evolution from a traditional automotive manufacturer to a comprehensive mobility company, capable of contributing to transportation solutions both on Earth and beyond, while fostering technological innovations that could benefit multiple industries and advance human exploration of space.