The post The Enduring Role of L-Band in Maritime Communications appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>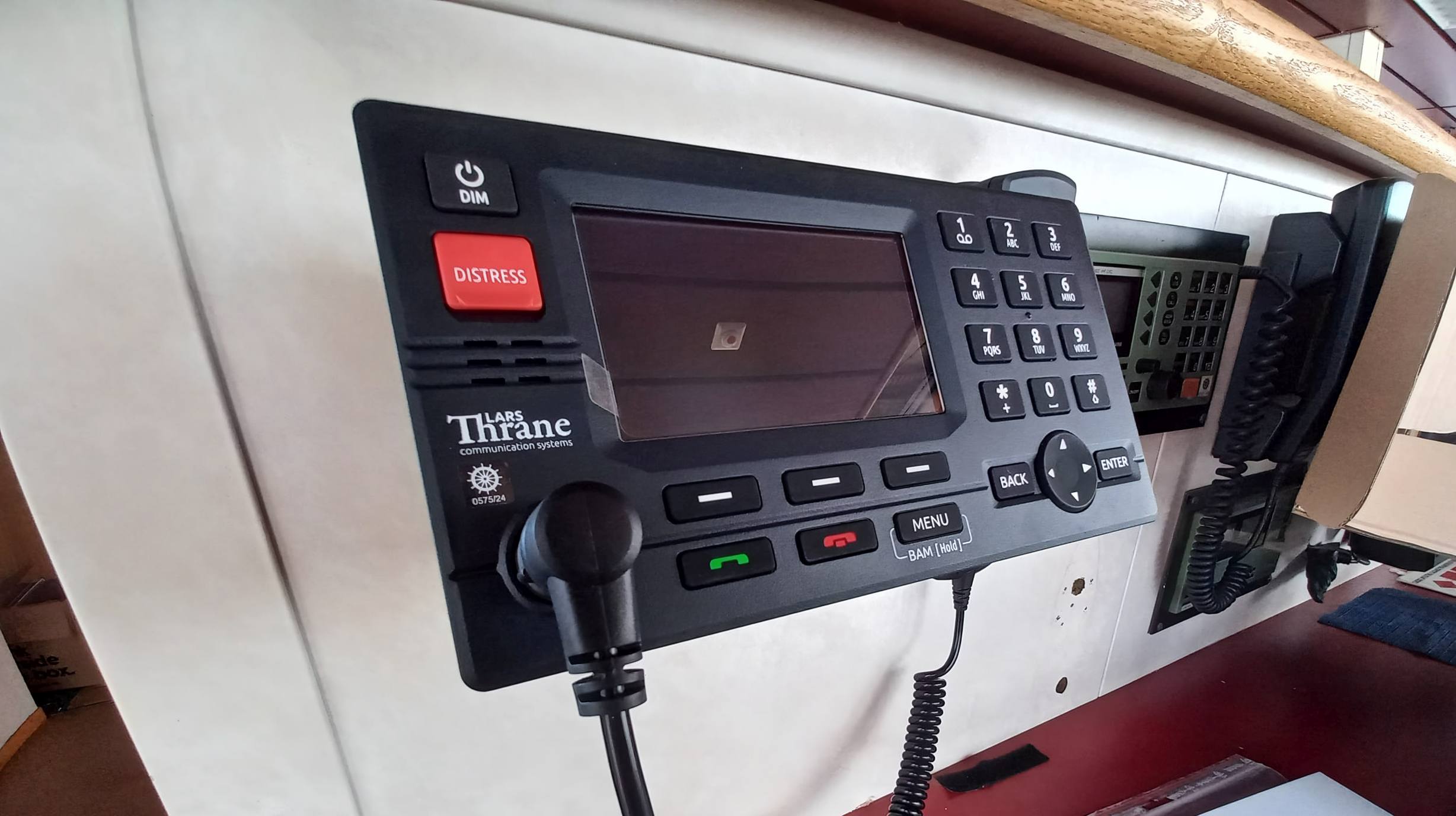 The Lars Thrane LT-3100S GMDSS System. Credit: Iridium
The Lars Thrane LT-3100S GMDSS System. Credit: Iridium
The main reason for maritime industry to rely on L-band services is regulation known as the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS). This is not an extra product that can be offered but a compulsory element for all commercial ships; therefore, L-band services are a crucial part of marine industry. Given the fact that L-band technology performs well in bad weather and during emergency situations, it has become the standard for maritime safety communications, providing the reliable link when other systems may not hold.
Market Value and Safety Applications
Thus, the L-band market showed impressive growth and reached $465 million in 2023 in spite of the decrease in value for the year before. Such stability is observed even in the context of new technologies coming into the market, which proves the indispensability of these services in the sphere of maritime activities. The L-band segment is expected to maintain a steady growth trend in the future according to the industry specialists due to the constantly growing level of the ship automation, new stringent safety requirements, and the understanding of the necessity of the backup communication systems in the modern maritime market.
The safety-oriented GMDSS market segment brings $213 million per year and is designed for approximately 78,000 ships globally. The global standards require at least two GMDSS terminals for the voyage in the case of the merchant vessels and the passenger vessels which are above 500 gross tones and in the case of the vessels with gross tones above 300, there should be at least one terminal set for the international voyage. The regulatory environment has provided a stable environment where this process of price change can take place without necessarily instigating market shocks. Price increases for basic safety services that took place in the industry over the last year generated over $30M in retail revenues worldwide, which proves the market’s viability.
Current Market Dynamics and Service Distribution
The broadband and voice services in L-band market covers more than 46000 ships globally and has a total sales value of $ 252 million. When incorporating backup systems, this number rises to around 62 000 of the currently operational ships with L-band broadband and voice solutions on board. This extensive market share is a clear indication of the importance of maintaining effective communications at sea; and, although the maritime industry is accustomed to employing various L-band solutions to provide seamless coverage across all the various maritime environments and climates, this particular system is preferred by many vessel operators as their primary means of communication.
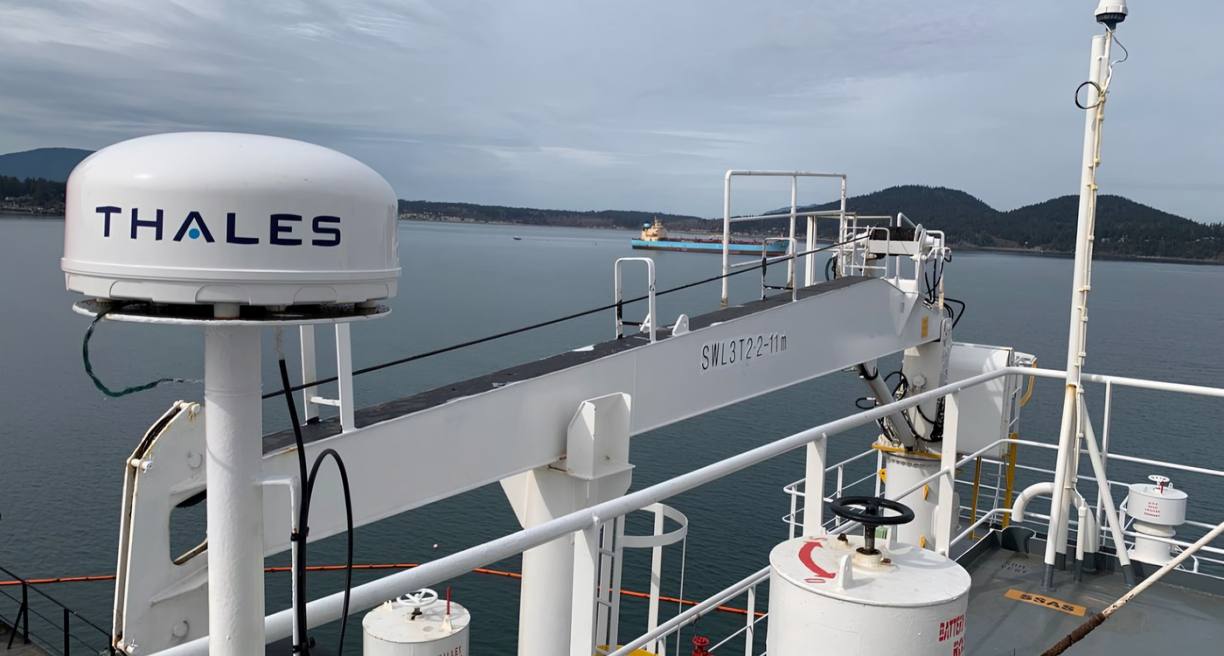 Thales VesseLINK 700. Credit: Google
Thales VesseLINK 700. Credit: Google
Competition in the market has shifted from being a provider market, among the service providers. Various services are currently specialized by need and location. For example, some services are chosen for fishing management applications and vessel monitoring services; others are selected based on their performance in the polar zones. Market distribution is seemingly healthy and diversified; traditional players continue to dominate the market, while new players can increasingly penetrate into the market due to technological advancement and offering lower prices. This healthy competition results to constant refinement of service quality and added utility.
Integration with Modern Maritime Communications
The maritime communications environment is gradually becoming a multilayered one where L-band services are a layer. Out of the 186522 ship with satellite subscription, more than 20000 are already using high speed LEO service proving the market trend towards dual connectivity. It is clear that the arrival of new technologies has not threatened the continued operation of L-band services. It has however, changed their role by positioning them as back up networks for the main broadband links. This evolution is in line with the increased importance of redundancy and reliability in the maritime business and especially in communications.
 Cobham SAILOR 4300. Credit: Google
Cobham SAILOR 4300. Credit: Google
The combined use of many satellite technologies has given service providers a new way of providing full connectivity solutions. These solutions utilize high speed of the newer systems with the reliability of L-band services regardless of the conditions. In addition, the growing need for timely data processing and improved organizational performance of satellite services will sustain the demand for L-band services, which are necessary for important applications such as tracking ships, receiving weather information, and conducting emergency calls. This three-tiered approach not only increases safety, but also minimizes cost in all aspects, which by extension is beneficial to the entire maritime environment.
Future Outlook and Technological Evolution
The L-band segment shows promising signs of stability and potential growth over the next decade. This optimistic outlook is supported by several key factors that reinforce the technology’s importance in maritime communications. Regulatory restrictions on newer technologies in certain regions highlight the continued relevance of L-band services. Many major shipping destinations and routes fall within areas where newer satellite services face operational restrictions, making L-band communications the only viable option for maintaining consistent connectivity.
The development of autonomous vessels further emphasizes the importance of reliable communication systems. L-band’s superior resistance to atmospheric interference and consistent coverage make it particularly valuable for automated maritime operations, where maintaining stable communications is crucial for safety and operational efficiency. Additionally, the growing demand for real-time data transmission and enhanced tracking capabilities will likely drive further investments in L-band technology, ensuring its ongoing significance in the evolving maritime landscape. As the industry adapts to new challenges, the L-band’s established infrastructure will remain a critical asset for maritime stakeholders.
 Intellian C700. Credit: Intellian
Intellian C700. Credit: Intellian
The maritime satellite communications industry stands at a fascinating intersection of tradition and innovation, where L-band services continue to prove their enduring value. Despite the emergence of new technologies and changing market dynamics, L-band remains fundamental to maritime operations for several compelling reasons. Its role in safety communications, global coverage capabilities, and reliability in adverse conditions makes it irreplaceable in the current maritime ecosystem. The technology’s resistance to interference, combined with regulatory requirements and the need for redundant communication systems, ensures its continued relevance. However, the key to maximizing these benefits lies in choosing a reliable service provider with proven expertise in the maritime industry.
BusinessCom has been delivering a wide range of maritime services for the past twenty years, equipping us with extensive knowledge of the challenges faced by vessel operators. We offer comprehensive solutions that combine reliability with today’s technological innovations. Our long-standing experience in the market, along with our deep technical expertise and personalized approach to each client, ensures that our maritime clients receive not only connectivity but also the ideal communication solution tailored to their needs. As the maritime industry shifts toward greater automation and higher connectivity requirements, we are here as your trusted partner to ensure that your maritime communication solutions remain effective, dependable, and prepared for the future.
The post The Enduring Role of L-Band in Maritime Communications appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post Astranis Confirms December 22 Launch Date appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>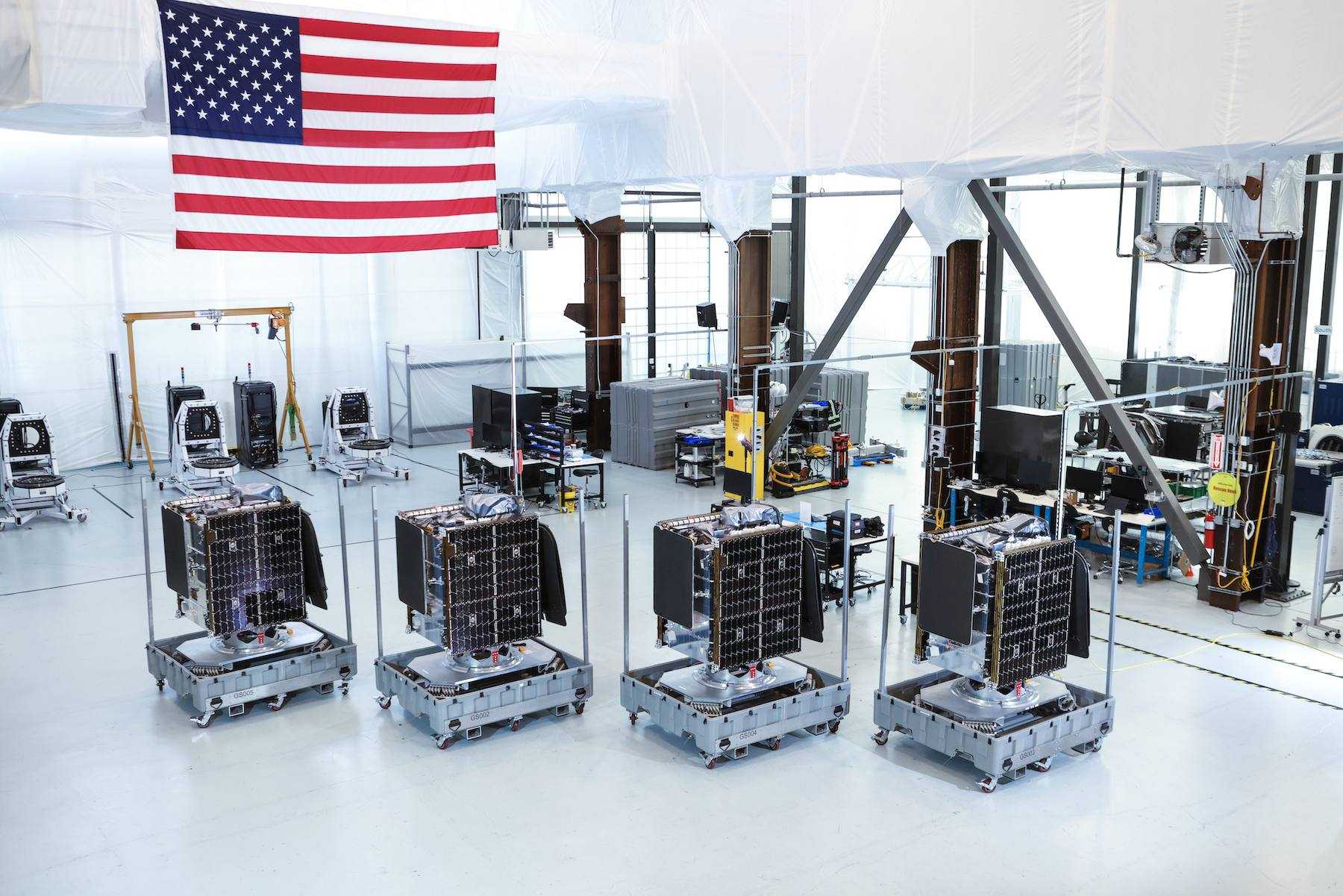 Astranis sends four MicroGEO satellites to Cape Canaveral for a Falcon 9 launch. Credit: Astranis
Astranis sends four MicroGEO satellites to Cape Canaveral for a Falcon 9 launch. Credit: Astranis
These satellites will be the first dedicated satellites used by Anuvu, and the company will be using satellites rather than leasing satellite capacity, which will be a first for the company. Anuvu CEO Josh Marks said the company’s goal was to grow its connectivity network in a way that would be both scalable and agile for its mobility customers. Astranis’s MicroGEO satellites would also give Anuvu’s customers the freedom from decades long contracts and out of date legacy systems, he added. Marks said the satellites’ quick market deployment, seven to ten year mission life, as well as their ground based control and update capabilities, would enable their mobility clients to adjust their business models as new technology comes to market.
The third satellite, called AGILA, is noteworthy because it is the Philippines’ first dedicated communications satellite. The development is a key partnership with regional satellite service provider Orbits Corp, which has already committed to building a second satellite for the Philippine market, showing strong confidence in the region’s growing telecommunications needs. Astranis’s commitment to multi-purpose functionality is demonstrated by the fourth satellite, dubbed UtilitySat. UtilitySat is designed to support multiple customers during its operational lifetime, though specific additional customers are not announced, and is also ordered by Mexico’s APCO Networks, which has already ordered two more Astranis satellites.
That launch will come after Astranis has experienced problems with its first MicroGEO satellite launched in April 2023 along with ViaSat-3. The vendor-supplied solar arrays on the inaugural satellite encountered problems that prevented the satellite from fulfilling its stated mission of providing broadband connectivity to Alaska. The current launch’s success has received heightened attention because of this setback. John Gedmark, CEO Astranis, pointed out the unprecedented nature of this mission and the fact that it marks the company’s first foray into managing multiple satellites at the same time. Launching four satellites at the same time represents a historic first in the industry, he said, noting that the satellites also include the most advanced technology to date, which will improve capacity and lower costs for their customers.
These four satellites represent the technical improvements Astranis has implemented to show its commitment to innovation. Upgrades to the MicroGEO model include a new in house developed gimbal for the electric propulsion thruster, a deployable main reflector to increase satellite throughput, and additional redundancy features in the company’s software defined radio system. If successful, the mission will be the first time that a single satellite manufacturer has placed four of its own satellites into geostationary orbit (GEO) on a single launch vehicle. It’s particularly notable, especially considering that Astranis satellites are orders of magnitude smaller than typical GEO satellites, which indicates that the company has been able to minimize launch and deployment costs.
The post Astranis Confirms December 22 Launch Date appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post Telesat Makes Waves in LEO Race with Lightspeed appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]> A Telesat Lightspeed satellite concept, featuring MDA’s software-defined platform. Credit: Telesat
A Telesat Lightspeed satellite concept, featuring MDA’s software-defined platform. Credit: Telesat
The preliminary design review has confirmed that the spacecraft design, which incorporates Canada-based MDA Space’s cutting-edge reprogrammable Aurora platform, aligns perfectly with the program’s functional and performance requirements. This validation demonstrates a major development toward realizing Telesat’s grand strategy of entering the LEO broadband market. Transitioning into a heavier engineering focus, the project is now in the process of progressing towards the crucial design review, which will decide if the 750-kilogram spacecraft is ready for production. Telesat has arranged 14 launches that are expected to start from mid-2026 and will launch all of its Lightspeed satellites within a single year, indicating the company’s strategy of a fast market penetration.
The manufacturing infrastructure is also being developed, with MDA starting construction of a new high volume manufacturing facility in Quebec, Canada. The potential of this facility to manufacture two satellites per day demonstrates that Telesat has grand industrial plans for the LEO market. In addition to the Telesat project, MDA has experience that it has accumulated in the satellite business. The company has recently won another contract of 180 million Canadian dollars (approximately $131 million USD) for preliminary engineering of a non-geostationary constellation of 36 satellites for an unknown client. This contract could potentially increase approximately four-fold if MDA is awarded the prime contractor for the constellation in the subsequent year.
The Lightspeed constellation’s technical specifications reveal its competitive positioning, with a planned capacity of approximately 10 terabits per second (Tbps). This substantial capacity targets various market segments, including backhaul services for mobile network operators, internet service providers, aviation and maritime connectivity solutions, and government customers. Similarly, Eutelsat’s OneWeb has successfully launched its satellites and is now providing broadband services with more than 650 satellites in orbit. Market trends are shifting rapidly and according to the Telesat’s CEO, Dan Goldberg, our competitors have proven that LEO broadband has certain competitive advantages. He stressed on volume and growth aspect of the market and also added that enterprise customer usually look for multiple players in the market thus giving multiple operators a chance in this field.
The satellite communications industry is currently marked by high growth rates and dynamic changes that are taking place, with several participants developing LEO constellations. The success of OneWeb, which has begun service after deploying over 650 satellites, and Amazon’s Project Kuiper, which aims to launch 3,236 satellites, indicates that the industry has a bright future ahead of it. This competitive environment with market veterans and newcomers demonstrates the significance of Telesat’s Lightspeed project. As these major constellations progress toward full operational capability, they collectively promise to reshape global telecommunications, bringing high-speed internet access to underserved regions and meeting the escalating demand for reliable, high-bandwidth connectivity across various sectors. The success of these parallel developments suggests that the future of global internet infrastructure will be increasingly space-based, with multiple operators working to connect the world’s population through advanced satellite technology.
The post Telesat Makes Waves in LEO Race with Lightspeed appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post Intelsat 33e Break-Up Reveals Space Security Gaps appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>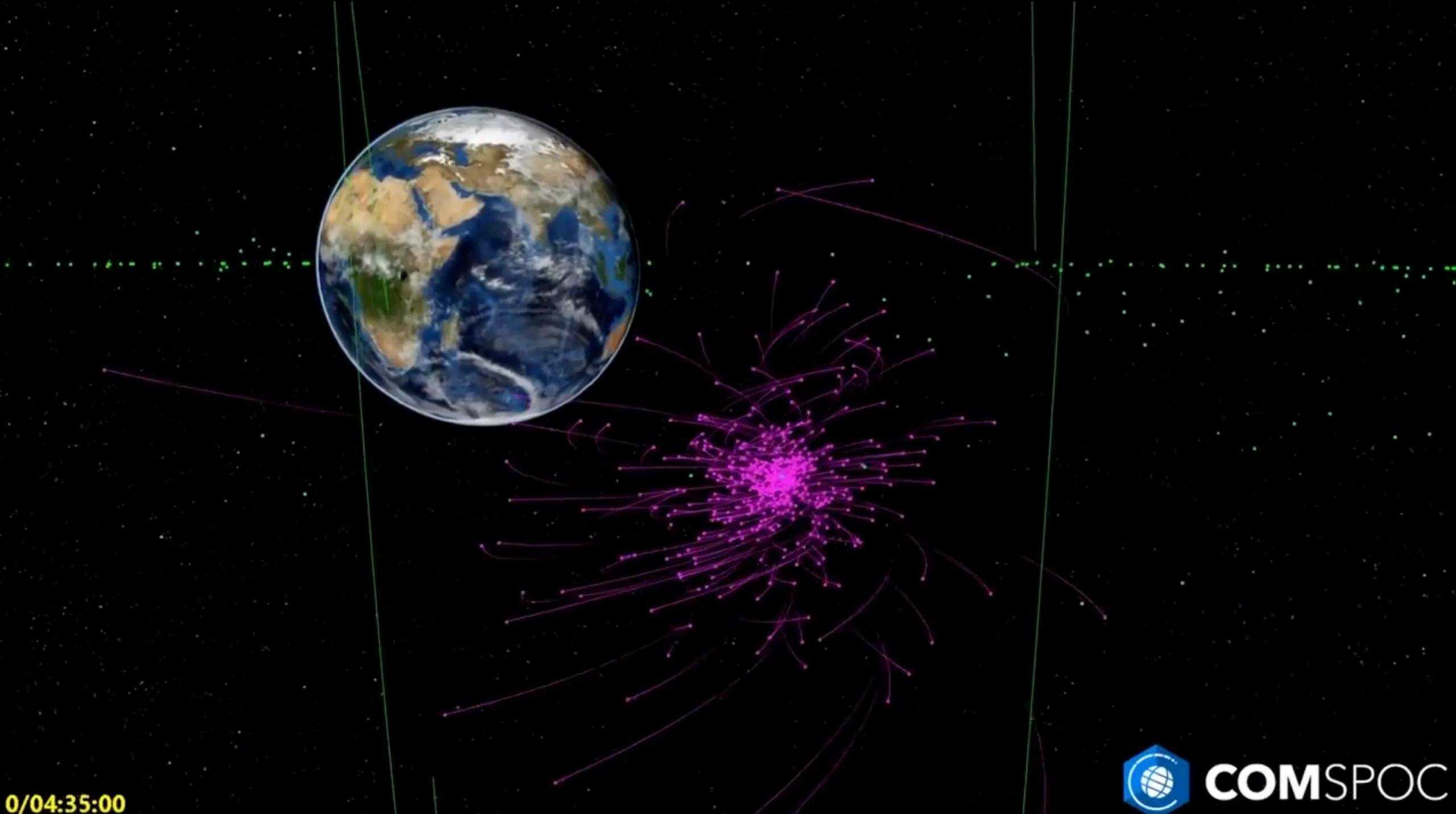 Visualization of Intelsat 33e break-up in GEO orbit. Credit: Comspoc
Visualization of Intelsat 33e break-up in GEO orbit. Credit: Comspoc
After the October 19th incident, the company’s chief growth officer, Clint Clark, said they had identified a large debris field of more than 700 pieces. In the initial assessment, 57 debris fragments were discovered, ranging from softball-sized to car door-sized pieces. Within a week, the number of debris pieces grew to about 500, potentially setting up an orbital environment that’s hazardous. Such a massive debris event could also be strategically useful to malicious actors, Clark warned. He said the chaos of the satellite breaking up could provide cover to launch more objects into the geostationary orbit and not be noticed. The strategic complexity of modern space operations and the opportunity for orbital incident exploitation is also a key theme in this observation.
The satellite’s break-up is the second in a string of four EpicNG high-throughput satellites built for Intelsat that Boeing continues to investigate. Intelsat-29e, the previous satellite in the series, was declared a total loss in 2019 and early reports blamed the failure on a meteoroid impact or a possible wiring flaw. On the panel on emerging space threats, ExoAnalytic Solutions executives highlighted the proliferation of space capabilities among global space powers, especially China’s expanding orbital presence. U.S. Space Force Headquarters’ intelligence directorate chief Master Sgt. Ronald Lerch mentioned the significant expansion of Chinese satellite infrastructure, from 36 satellites in 2010 to thousands in recent years.
Space tracking professionals have observed increasingly sophisticated maneuvers by Chinese satellites, including routine close-up inspections of other orbital objects. What appear to be direct-ascent threat practices have been tracked by ExoAnalytic Solutions, indicating a more complex and even potentially confrontational space environment. Lerch noted that these capabilities have allowed what he called ‘norm shattering behaviors,’ specifically in strategic instances like China’s rising presence in or near Taiwan. It has huge implications for global space security. The proliferation of satellites and the growing number of orbital disruptions demand that international protocols and sophisticated monitoring systems be developed as soon as possible. The potential for strategic disruption increases with the increase in space as a contested domain. Experts said since the Intelsat 33e incident, collision alert systems have stabilized after an initial spike. But the event is a reminder that our orbital ecosystem is fragile and dynamic. With satellite debris, potential strategic manipulations and the increasing space faring capabilities of nations, unprecedented levels of technological sophistication and international cooperation are needed.
Intelsat 33e incident shows that space structure is even more complex than was known before and highlights the critical point in the space security history. It proves that space is not the territory anymore but rather a dynamic and tangible battlefield where technology opportunity, conflict, and scientific risk collide. The accelerated space object placement density together with the possibility of orbital debris stimulating discussed strategic machinations, requires a system strategy to preservation and management of space environment. Collectively, the nations and private entities must invest in enhanced tracking technology as well as international protocols and supervise the sustainable management of the more congested space orbits.
The post Intelsat 33e Break-Up Reveals Space Security Gaps appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post Intellian Launches Cutting-Edge Antenna Line appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]> OW10HL promo. Credit: Intellian
OW10HL promo. Credit: Intellian
The innovative terminals, which are a remarkable advancement in satellite communication technology, are designed to meet various service requirements. The new active electronically scanned array (ESA) user terminals have been designed for fixed, land mobility and maritime services. These terminals are particularly interesting, as they are the smallest terminals in the Eutelsat OneWeb portfolio, and are only compatible with the OneWeb Low Earth Orbit (LEO) network. These antennas are impressively compact and versatile in their technical specifications. The footprint of each terminal is less than two feet long and is precisely 22 inches wide by 17.7 inches deep by 4.7 inches high. All three terminals have a consistent weight of 26.9 pounds, which is lightweight and deployable to many environments and applications.
These terminals are designed by Intellian to cover various use cases in the different industry sectors. The land terminal (OW10HL) is developed strategically for small enterprise operations, cellular backhaul infrastructure, and governmental communication purposes. It is the land mobility terminal, OW10HV, which is specifically engineered for critical sectors including emergency first responders, transportation services, agricultural operations and forestry management. The maritime terminal, OW10HM, is optimized for fishing vessels, leisure boats and smaller maritime craft. Specific details of download speeds and individual unit pricing are not disclosed, but the terminals are only available through authorized resellers. Intellian’s commitment to its satellite communication portfolio continues through the wide range of flat panel antennas. Six flat panel antennas for the OneWeb network are now in the company’s portfolio, including the new three terminal OW10 series and three others in the larger OW11 series. The OW11 series terminals are a bit heavier at around 45 pounds.
These technological advancements have received the stamp of approval from industry leaders. According to Javier Santolaria, senior director of User Terminal Development and Production at Eutelsat OneWeb, partners and end users have given exceptionally positive initial feedback on the performance and user friendliness of these terminals. For the company, these developments are considered a major breakthrough in satellite communication technology. Intellian Technologies’ Vice President of ADC Product Management, Toni Kousiafes, commended the importance of this product launch. The new terminals, he said, show the company’s technical and manufacturing capabilities at the forefront and herald the start of a new connectivity era for Eutelsat OneWeb customers. ‘Flat panel antennas are the market of the day, and we are excited about the potential impact of these innovative products across the industry,’ said Kousiafes.
Intellian Technologies is a world leader in satellite communication solutions since 2004. Irvine, California, United States, is the company’s headquarters. Innovation, reliability and advancing global connectivity through cutting edge satellite communications technologies are the core of their corporate manifesto. Intellian is committed to exploring innovative technological frontiers, delivering sophisticated communication solutions to address the ever changing needs across a wide range of industries around the globe.
The post Intellian Launches Cutting-Edge Antenna Line appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post ST Engineering iDirect Unlocking the Multi-Orbit Era appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]> The ST Engineering iDirect promo booth at SATELLITE Conference and Exhibition in Washington D.C. Credit: ST Engineering iDirect
The ST Engineering iDirect promo booth at SATELLITE Conference and Exhibition in Washington D.C. Credit: ST Engineering iDirect
In recent years, the satellite communications market has been through major restructuring with the incumbents having to respond to changing market dynamics and innovation. It has experienced a rising trend in investment, technology, and cooperation that has redefined the structure of the industry. These developments have presented problems and opportunities for the incumbent providers to adapt to a new business model and ways of working. The emergence of new market entrants have brought new ideas and fresh strategies into the market they have sparked the change across the whole sector.
Strategic Integration
The industry’s opinion on various orbits and standards has changed a lot, especially, ST Engineering iDirect’s CEO Don Claussen who urged to reconsider business models. The drawbacks of both vertically integrated and horizontal models were emerging to the forefront more and more often; the former focused on the issue of ownership and dominance rather than open integration, while the latter could sometimes be too rigid in their functioning. However, the gaps in the business strategies of the acquisitions were not closed, and Claussen’s advocacy of diagonal integration offered a new solution that would facilitate the link with telecommunications providers and wireless carriers. The approach stressed the fact that the various orbits should not be considered as rivals but rather as future networks will likely contain a mix of orbital solutions.
 ST Engineering iDirect’s INTUITION promo. Credit: ST Engineering iDirect
ST Engineering iDirect’s INTUITION promo. Credit: ST Engineering iDirect
This strategic change has come with a shift in perceptions of the industry players about cooperation and rivalry. Traditionally, companies have focussed on safeguarding their technologies and running relatively isolated systems and this model has evolved. Business entities are slowly starting to realize that the current satellite business environment cannot be conquered by a single entity and that compatibility is the key to success. It has also resulted in emergence of new cooperative structures between the earlier competing parties, arising out of the need to find new business models and markets.
Technological Advancement
The industry was characterized by a new trend in customers’ behavior and their desire to choose solutions offered by several vendors rather than focusing on a specific industry giant. Speaking on the same, the Senior Vice President of Engineering, Sridhar Kuppanna said that there is a clear trend towards standards based integration especially with the emergence of 5GNNT technology. Some of the difficulties experienced during the integration process included; roaming and the integration of support structures. Standards-based APIs and end-to-end orchestration were introduced as essential aspects that would help to integrate space and ground solutions efficiently. This technical evolution meant that existing assets had to be taken into account while at the same time building for future capacity.
Satellites are not only being developed in terms of the better hardware but have also been endowed with highly developed software solutions and networking. Satellite networks have benefited from the incorporation of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the way that these networks are managed and supported. They have facilitated better use of resources, increased the quality of service delivery, and increased reliability of networks. The commitment level of this industry in innovation has ensured that major advancements are recorded in areas such as beam forming, signal processing, and network optimization, opening up new opportunities for satellite communications.
Market Dynamics
The industry landscape has been significantly impacted by vertical strategies from companies like SpaceX and horizontal consolidations such as the SES/Intelsat and Viasat/Inmarsat mergers. These developments have created new challenges related to infrastructure management and interoperability. The concept of a “network of networks” has emerged as a critical framework for future development, emphasizing the importance of compatibility and seamless connectivity across different systems. Industry groups like DIFI, WAVE consortiums, and 3GPP standards have played vital roles in enabling diagonalization and cross-vendor interoperability.
 ST Engineering iDirect HQ. Credit: Google
ST Engineering iDirect HQ. Credit: Google
Market dynamics have been further complicated by evolving customer expectations and demands. Both enterprise and consumer markets are seeking more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective satellite communications solutions. This shift in demand has driven innovation in service delivery models and pricing structures. The industry has responded by developing new business models that better align with customer needs, including pay-per-use options and customizable service packages. These changes have created new opportunities for market growth while introducing additional complexity to the competitive landscape.
Future Direction
The transformation of the satellite industry encompasses not only technological advancements but also innovative, strategic new ideas and flexible approaches to service delivery. The comprehensive shift of focus towards telco value addition and network intelligence revealed a new paradigm. The idea of diagonalization was no longer just a buzzword within the satellite industry but actually signifying a complete overhaul of satellite industry strategies. This dynamic, transformative evolution was supposed to provide continuity in different orbits and networks and give the industry more opportunities for further development and new technologies.
The satellite industry experience is therefore a shift from the traditional operational models to the integrated and connected future. As a result of this transformation due to technology development and other market factors, new strategies of operation and provision of services have been required. As the sector develops further the role of standardization, interoperability and integration will grow, resulting in further enhanced SATCOM systems. This transformation will be successful by the extent to which the industry offers dependable, ubiquitous, and inexpensive connectivity solutions to the users internationally.
The post ST Engineering iDirect Unlocking the Multi-Orbit Era appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post Orbital Services Startup Starfish Space Raises $29M appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]> Starfish Space’s Otter vehicle promo. Credit: Starfish Space
Starfish Space’s Otter vehicle promo. Credit: Starfish Space
Starfish Space is founded by seasoned engineers with deep backgrounds in Blue Origin and NASA, and have developed state of the art autonomous satellite servicing vehicles to solve critical problems of orbital maintenance. It’s already working in partnership with commercial satellite company Intelsat in a key partnership, already boasting a $37.5 million contract with the U.S. Space Force, and it’s at the vanguard of disruptive space infrastructure management and debris mitigation technology.
Starfish’s Otter satellite servicing vehicle will be developed, launched, and operated in geostationary orbit by 2026 under a four year Strategic Funding Increase (STRATFI) Space Force contract. The $37.5 million in government funding and the additional $30 million from venture capital investments into the project are indicative of a growing interest in advanced space maintenance technologies. In a search for new ways to improve orbital satellite maneuverability, military space strategists are exploring different options. Otter type spacecraft in-orbit refueling and servicing can be promising. Space Systems Command Colonel Joyce Bulson said Otter’s capabilities are more than just simple maneuvering, including station keeping, life extension, orbital transfer, and ultimately, responsible orbital disposal.
SpaceWERX, the Space Force’s technology division, has previously awarded the company Small Business Innovation Research contracts. They launched a demonstration mission called “Otter Pup” in low Earth orbit in 2023, but an anomaly struck and the mission was not fully successful. But nonetheless, Starfish Space keeps pushing the envelope with technology. STRATFI agreements are fundamental to the Defense Department’s strategy in bridging the critical funding gap between technological development and actual application. These agreements allow innovative companies like Starfish Space to take cutting edge concepts and turn them into operational solutions that meet military needs.
The Tukwila, Washington company, Starfish Space, recently hit a funding milestone that will enable it to close out its first trio of Otter vehicles, and bring cumulative investments past $50 million. The spacecraft are designed to fly specific deployments to geostationary orbit in 2026 to conduct critical Intelsat, U.S. Space Force and NASA missions. Starfish Space’s satellite servicing technologies represent a revolution in space exploration, providing levels of satellite maintenance, operational efficiency, and economic viability beyond anything previously achieved through comprehensive satellite maintenance and responsible orbital management in increasingly complex orbital environments. In light of the increasing space debris, the company is well situated to tackle this growing challenge and to build advanced in orbit servicing technologies to assure the continued long term usability and safety of critical satellite infrastructure and supporting worldwide communication, navigation and scientific research efforts.
The post Orbital Services Startup Starfish Space Raises $29M appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post Apple and Globalstar Partner on New Satellite Constellation appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]> Apple iPhone satellite locator. Credit: Apple
Apple iPhone satellite locator. Credit: Apple
The project, which is separate from Globalstar’s ongoing constellation upgrade with MDA Space, is an extension of the company’s satellite infrastructure. The investment includes not only the development and launch of a new mobile satellite services constellation but also substantial ground infrastructure improvements. Under the terms of the agreement, Apple has committed to reserving 85 percent of the network’s capacity for use by its own services, a sign of just how deep the partnership between the two companies really is. Key elements of the financial structure of the deal comprise strategic provisions for Globalstar’s stability and growth. The $1.1 billion part is a prepayment for the use of the new network to provide expanded satellite services, plus $232 million to pay down debt. These financial arrangements allow Globalstar to continue to maintain strong operational capability while undertaking this ambitious expansion project.
Paul Jacobs, Globalstar’s CEO, has confirmed that work on the new constellation program is already under way, but details about satellite manufacturers and project timelines are not yet available. The announcement has sent shares in the company soaring, as reflected in the market’s confidence in the expanded partnership with Apple. Globalstar is continuing its existing constellation refresh program by ordering 17 satellites from MDA Space and the option for 9 additional units. It follows an existing successful collaboration between the two companies. Since November 2022, Apple has integrated satellite capacity into standard phones, and is the first phone manufacturer to do so, using Globalstar’s satellite capacity for its emergency messaging service on the iPhone 14. In addition to emergency messaging, the service has expanded to include standard messaging in places where cellular or Wi-Fi are not available, exhibiting the real world utility of satellite to phone.
Competition in the satellite-to-phone communication industry is growing broader. Apple was the first to bring these services to the mass market, but others are joining forces with satellite operators to develop similar capabilities in collaboration with equipment manufacturers and mobile network operators. In the United States, companies such as AST SpaceMobile partner with major carriers such as AT&T and Verizon, and mobile network operators in other countries. This partnership has evolved in tandem with the increasing need in consumer electronics and communications for satellite connectivity. With the growing use of satellite to phone technology, Apple’s strategic investment in Globalstar’s new constellation puts both companies in a position to make a big impact on how the world connects. It’s a major milestone for both companies, but also a sign of a larger shift in how consumers may get communications services in the years ahead.
The post Apple and Globalstar Partner on New Satellite Constellation appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post Kymeta Launches Goshawk u8 Multi-Network Terminal appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]> Goshawk u8 promo. Credit: Kymeta
Goshawk u8 promo. Credit: Kymeta
As a hybrid terminal, the Goshawk u8 is unique for its support for multiple connectivity options including Geostationary (GEO), Low Earth Orbit (LEO), and cellular networks. This new product offering expands Kymeta’s product portfolio of multi-orbit, multi-network, modem agnostic solutions following the successful launch of their military focused Osprey u8 HGL terminal in 2023. The terminal is designed to enable seamless mobility across multiple vehicles and vessels, while the company’s strategic partnership with OneWeb for LEO connectivity adds to the terminal’s capabilities. Goshawk u8 has an array of technical specifications which meet its operational requirements. Embedded LEO and cellular modems are available, along with comprehensive Wi-Fi support, and compatibility with external GEO modem connections. One of its most advanced technology is its jamming mitigation capabilities for GNSS denied operations, which make it especially suitable for defense forces and other high demand industries that demand reliable communication solutions.
According to Kymeta’s president and CEO Rick Bergman, the development of the Goshawk u8 was driven by increasing market demands for robust mobile connectivity in challenging environments. The executive emp͏hasized͏ that the ͏terminal’s software-defined capabilities ensure consistent and secure c͏omm͏unications, e͏ven i͏n͏ the ͏most re͏mote a͏nd deman͏ding conditions.
The terminal’s sophisticated multi-orbit capabilities provide for enhanced availability and flexibility for users in applications ranging from military to civil. It is engineered to offer a low power, low profile design that is easy to deploy and operate, making it of particular value to defense forces and other industries operating in challenging environments. Under the most demanding operational conditions, the terminal’s robust performance capabilities guarantee reliable communication. This latest innovation further solidifies Kymeta’s position as an industry leader in flat panel intelligent communications platforms. Using their metasurface technology in combination with a software first approach, they have brought to market the first metamaterial based and electronically steered flat panel satellite antenna. The company’s solutions are characterized by their cost effectiveness, high energy efficiency and high throughput capabilities, and thus suitable for connecting different platforms, mobile or stationary.
Kymeta’s technology has broader impact across multiple sectors, including enterprise and military, to meet the increasing need for reliable broadband connectivity worldwide. They are at the forefront of solving connectivity challenges worldwide by their innovative approach to unlock the commercial value of space. Kymeta’s continuous technological advancement enables industries to improve their operations by taking advantage of space based communication capabilities to achieve consistent connectivity while anywhere or in any movement conditions.
Kymeta C͏orporation, founded in ͏2͏0͏12 by͏ N͏athan Kundtz in Redmond, Was͏hin͏gton, sp͏ecializes in͏ developing inno͏va͏tive satellite commun͏icati͏on technolo͏gies throu͏gh ͏its uniq͏ue͏ flat-panel ante͏nn͏a sy͏stem͏s.͏ Th͏e͏ co͏mpa͏ny ͏has secu͏red over $3͏00 mi͏l͏lion in funding fro͏m inves͏tors including͏ Bill Gates͏ and op͏erates under the le͏adersh͏ip of CEO Rick Bergm͏an. W͏ith its mi͏ssion to make mobil͏e connectivity gl͏o͏ball͏y accessible, Kymeta continues to͏ re͏v͏o͏lu͏tionize satelli͏te communications by providing reliabl͏e soluti͏ons for vario͏us platforms͏ worldwide.
The post Kymeta Launches Goshawk u8 Multi-Network Terminal appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>The post Boeing Launches Quantum Space Mission appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>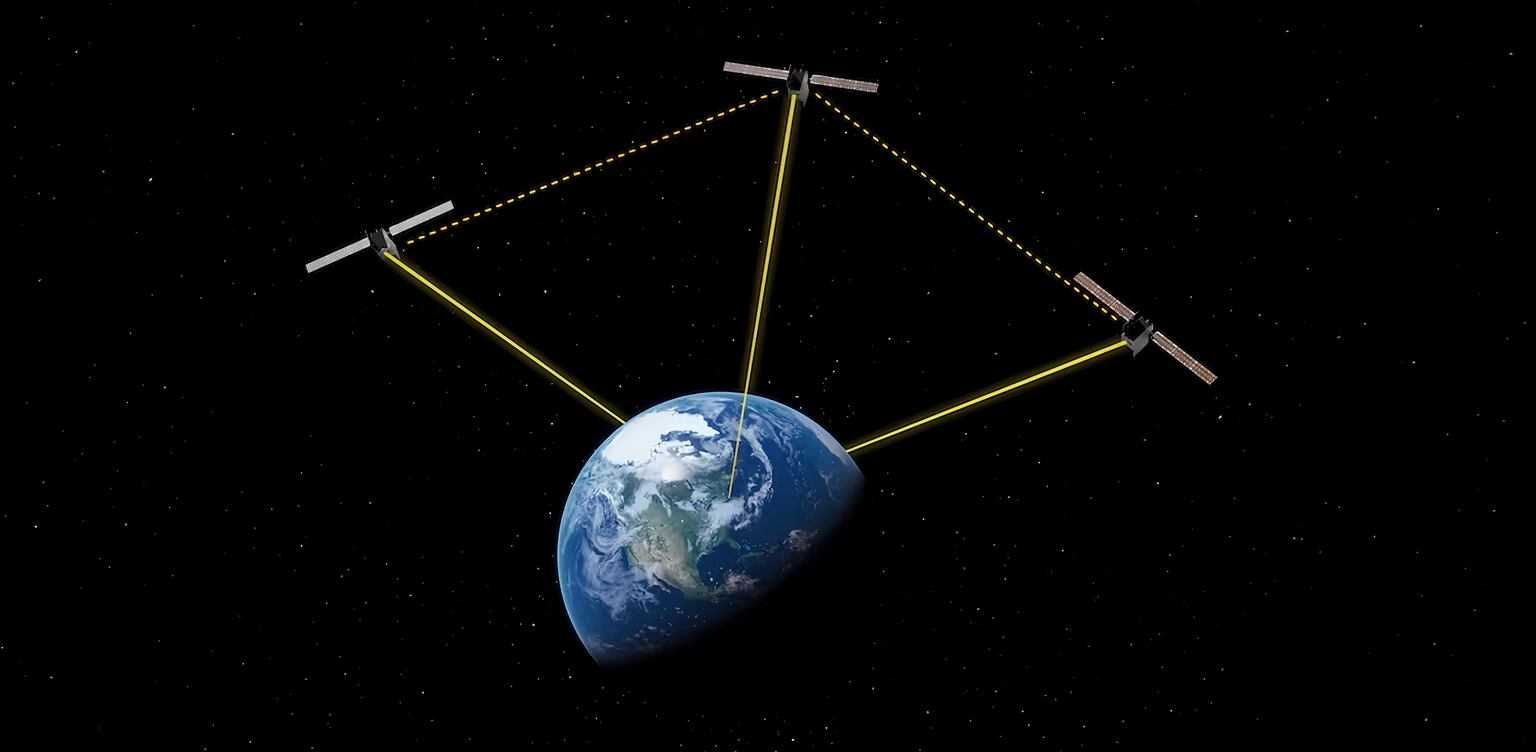 Boeing’s Q4S mission aims to enable space-based quantum internet. Credit: Boeing
Boeing’s Q4S mission aims to enable space-based quantum internet. Credit: Boeing
Beyond its technical achievements, the significance of this Boeing funded mission extends far beyond to revolutionize many secure applications such as fault tolerant computing systems, secure voting mechanisms and blind quantum computing. This mission is a cornerstone of Boeing’s quantum portfolio strategy, said the chief engineer for Boeing’s Disruptive Computing, Networks & Sensors organization, and it is one the company is willing to take calculated risks on to better understand how new technologies may impact Boeing products and services.
Understanding Quantum Entanglement
Quantum teleportation is a famous example of the phenomenon of quantum entanglement, described by Albert Einstein as ‘spooky action at a distance’, and is the amazing process where information carried by particles can be transferred without physical movement over distances. Specifically, Q4S focuses on quantum entanglement swapping, a sophisticated procedure for the exchange of quantum information between network segments, without direct contact, which distinguishes it from previous quantum missions that primarily dealt with quantum key distribution protocols. If this new breakthrough approach to information transfer truly delivers on its promises, it could revolutionize our understanding of communication networks and open up options that were previously the stuff of science fiction.
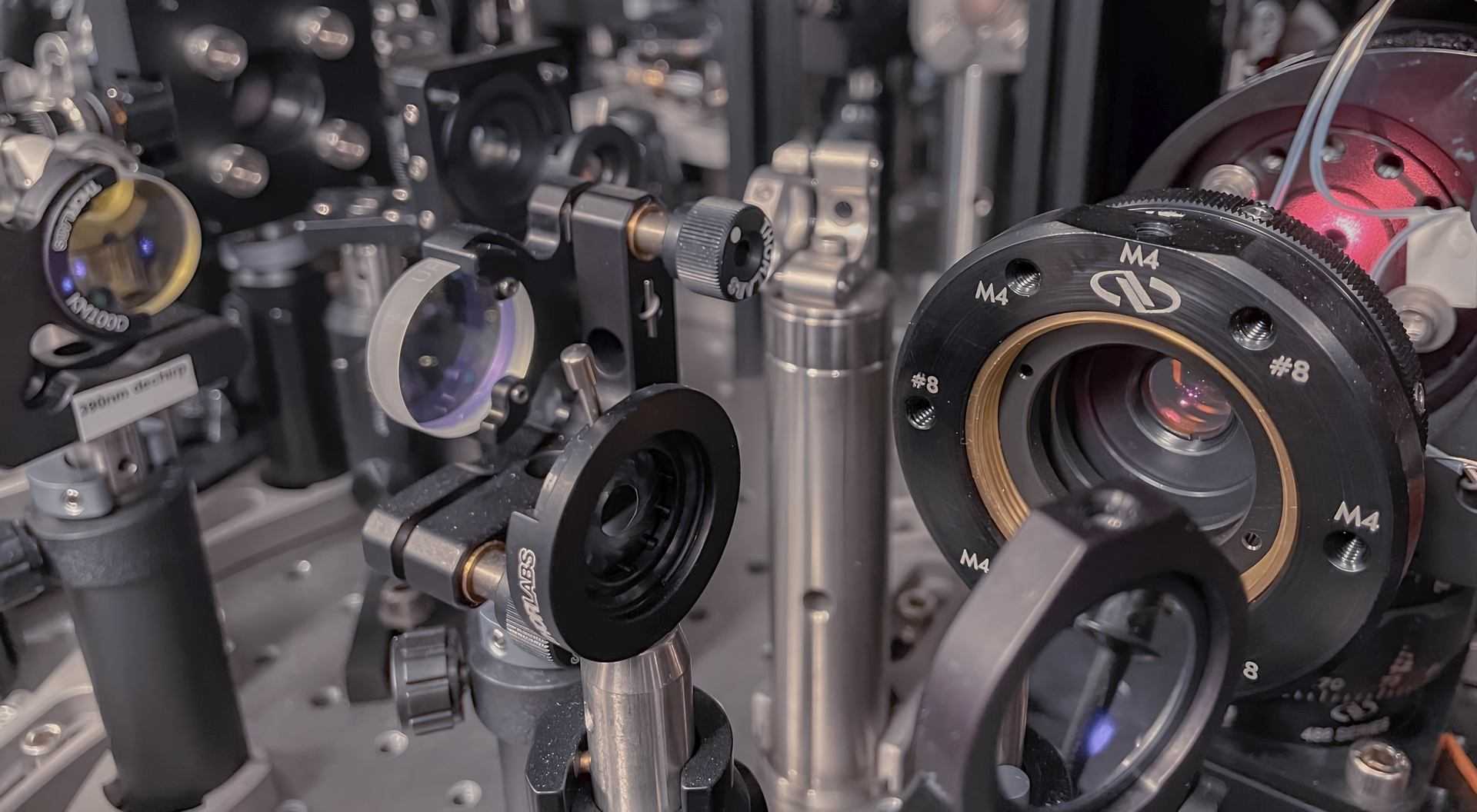 Boeing and HRL’s quantum entanglement lab prototype. Credit: Boeing
Boeing and HRL’s quantum entanglement lab prototype. Credit: Boeing
Quantum entanglement has been demonstrated in the laboratory, but its use in space is an unprecedented challenge. This advancement was made possible by the 2019 SpooQy-1 mission from the National University of Singapore, which showed that an entangled photon pair source can be operated in a cubesat. However, Boeing’s mission further takes this concept to the next level by realizing advanced quantum entanglement swapping protocols on a smallsat platform, while the mission itself does not involve direct quantum computation in orbit. Successful space based quantum entanglement has technological implications across a range of scientific research and practical applications. The potential for this advancement is in the development of ultra secure satellite communications, quantum based navigation systems and even to shed some light on the fundamental physics principles in space environments. Maintaining quantum states in the harsh environment of space represents a major leap forward in our ability to harness quantum phenomena for practical applications, and now could open new frontiers in space exploration and satellite technology.
Technical Challenges and Laboratory Success
Boeing and HRL Laboratories have been systematically addressing the technical hurdles to the translation of laboratory physics experiments to orbital operations. Entanglement swapping has already been demonstrated successfully in laboratory conditions using components that are representative of the planned payload design. Rigorous component and subsystem environmental testing is being used to demonstrate functionality in the space environment which is very different from controlled laboratory conditions. In addition, extensive testing program has been carried out on advanced simulation techniques and special equipment to perform the extreme temperature variation, radiation exposure and vacuum conditions in space.
Meticulous attention to detail and ingenious solutions have been necessary to overcome the unique challenges presented by the space environment during the development process. To do this, the engineering team has built robust systems capable of keeping the quantum states that are critical for entanglement swapping, and that can withstand the extreme conditions of space travel and operation. It is this delicate balance between quantum stability and physical durability that has enabled breakthroughs in materials science and engineering design to expand the limits of what is possible in space based quantum systems.
 Boeing’s Q4S promo. Credit: Boeing
Boeing’s Q4S promo. Credit: Boeing
Several technological innovations for space based quantum operations have been developed as part of the collaborative effort between Boeing and HRL Laboratories. New methods for thermal management of sensitive quantum components, radiation hardened control systems and precise alignment mechanisms which maintain stability during orbital maneuvers are included in these advances. The team has also developed highly sophisticated error correction protocols and redundancy systems to run the mission for its entire duration, taking advantage of learning from previous space missions and quantum experiments. Their work has set new standards for space qualified quantum hardware that could be leveraged for future missions across the aerospace industry.
Future Applications and Network Potential
This quantum communication technology promises to be a successful implementation in multiple sectors such as computing, healthcare, finance and telecommunications. According to Boeing, the hybrid network will use satellites to carry long haul traffic and fiber optics for short haul quantum information transfer. It provides more security features, including the ability to verify network node locations to prevent unauthorized access or manipulation. Beyond basic communication security, this capability has potential applications in advanced interferometric measurement imaging that could change the game in global resource monitoring, including precise tracking of water levels and emissions data. Boeing, which is cautious about setting specific timelines for a comprehensive quantum communications network, said it has seen significant interest from commercial and defense sector customers in exploring the possibilities of this groundbreaking technology.
Boeing’s Q4S is a critical step in quantum communications technology development, connecting the theoretical physics to real world applications in space. If quantum entanglement swapping in orbit can be demonstrated successfully, it could herald the start of a new era of secure communications and data transfer that will have far reaching repercussions beyond any one industry. However, the mission’s ambitious goals and use of an innovative approach reflect the critical role that quantum technology will play in defining the future of global communications infrastructure. By developing this technology, Boeing is not only showing the world how it pushes the limits of what is possible in space based communications, but is showing the world how quantum physics principles can be applied to solve real world problems. However, as the project marches toward its 2026 launch date, it is a testament to human ingenuity and the continuing evolution of our technological capabilities, and may well set the stage for a future in which quantum communications become a part of our global information infrastructure.
The post Boeing Launches Quantum Space Mission appeared first on BusinessCom Networks.
]]>